Abstract
Introduction: Portal vein embolization or ligation (PVE/PVL) is part of most multi-stage liver procedures in the case of low future liver remnant volume (FLRV). PVE initiates compensatory hypertrophy of non-occluded liver parenchyma. This hypertrophy is stimulated by an increased volume of portal blood in the non-occluded veins. PVE results in adequate FLRV growth necessary for resection only in 63-96% patients. The aim of this publication is to summarize the possibilities of influencing liver regeneration after PVE/PVL in an experiment using cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6), a monoclonal antibody against TGF-β1 (MAB TGF-β1) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSC).
Methods: The experimental model of PVE/PVL was chosen as best compatible for potential use in human medicine. 9 (control group), 9 (TNF-α group), 8 (IL-6 group), 6 (MSC group) and 7 piglets (MAB TGF-β1 group) were enrolled in individual studies. We performed laparotomy with PVL of the right-sided liver lobes under general anaesthesia. The following amounts of substances were applied in the non-occluded portal vein branches immediately after PVL: physiological solution (control group), recombinant porcine TNF-α (5 μg/kg), recombinant porcine IL-6 (0.5 μg/kg) and MSC (8.75, 14.0, 17.0, 17.5, 43.0 and 61.0 x 106 MSC). MAB TGF-β1 was applied 24 hours after PVL (40 μg/kg). Biochemical parameters were analysed repeatedly and FLRV ultrasound assessments were performed in the postoperative period. The experiments were ended on postoperative day 14 by sacryfiing the animals under general anaesthesia. Liver samples of hypertrophic and atrophic liver parenchyma were analysed.
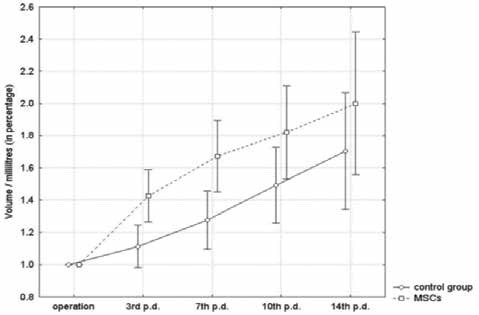
Results: Repeated ultrasound assessments of the effects of MSC, TNF-α, IL-6 and MAB TGF-β1 compared with the physiological solution in the control group demonstrated statistically significant acceleration of FLRV growth in the experimental groups. For MSC, maximum growth was observed between postoperative days 3 and 7, on day 7 for TNF-α, between days 3 and 7 for MAB TGF-β1 and on day 7 for IL-6. Serum levels of AST and ALT increased after PVL and MSC whereas other biochemical parameters showed no statistically significant differences. We identified individual MSC using immunohistochemistry in the hypertrophic tissue of the MSC group. A statistically significant difference was observed in the number of binucleated hepatocytes, with their increased concentration in the IL-6 group.
Conclusion: Application of IL-6, TNF-α, MAB TGF-β1 and MSC seems to provide suitable stimulation for achieving faster FLRV growth. Nevertheless, many controversial questions still remain to be answered with respect to the mechanism of their respective effects.