Abstract
Introduction: Despite current efforts at the most conservative approach possible to splenic injury, splenectomy remains a relatively common surgical procedure. Indications for splenectomy, however, are not limited to spleen injury. In senior patients in particular, non-traumatic reasons for splenectomy becomemore frequent. In addition, previous studies have indicated a relatively wide range of complications and lethality in splenectomized patients without taking into account the age aspect. Within the scope of geriatric surgery, this study deals with splenectomy in elderly patients and is based on retrospectively evaluated experience of our clinic.
Method: We studied a group of patients older than 65 years having undergone splenectomy at our institutionover the past 11 years. For each patient, the demographics, the reason for splenectomy, the mechanism of injury (if any), the degree of spleen damage, co-morbidities, the length of hospital stay, complications and lethality were evaluated. A group of patients operated on due tospleen trauma and the other group operated on for other reasons were analysed separately. Attention was paid to the reasons leading to splenectomy in the non-traumatic patients. Complications and lethality rate were evaluated in relation to the individual patient groups.
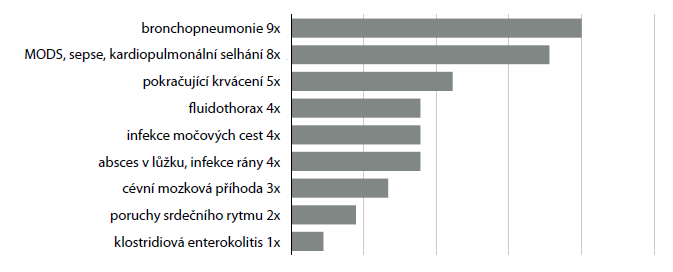
Results: 269 splenectomies were performed in our clinic between 2006 and 2016. Of these, only 57 (21.2%) were carried out in patients older than 65 years (32 men and 25 women aged 65−90, mean age 73.6). Splenectomy was even rarer in association with splenic trauma:it was performed in only 13 senior patients. Other causes leading to splenectomy in elderly patients were: perioperative spleen injury (17 patients), gangrene, septic activation or spontaneous rupture of the spleen (10 patients), splenectomy during an operation on another organ (8 patients), splenomegaly (5 patients) and splenic artery aneurysm (4 patients). Lethality in the entire group was 29.8%, the percentage of complications was 57.9%; however, circumstances leading to splenectomy and also potential co-morbidities played a significant role. The average length of hospitalization in the entire group was 20.3 days.
Conclusions: Splenectomy in patients over 65 years of age is associated with a high risk of complications and very high lethality. However, senior patients after splenectomy for monotrauma and those after elective splenectomy have a very good prognosis.