Abstract
Introduction: Acute calculous cholecystitis is a common disease treated mostly by surgical therapy – laparoscopic cholecystectomy (CHE), particularly upon the common failure of conservative therapy. Timing of the surgery is essential for the development of perioperative complications.
Methods: We carried out a retrospective study with patients hospitalised at our Department of Surgery, University Hospital Královské Vinohrady between January 2013 and December 2015 for the treatment of acute calculous cholecystitis. We had a set of 209 patients. We looked for the presence of perioperative complications in relation to the time of surgery – cholecystectomy.
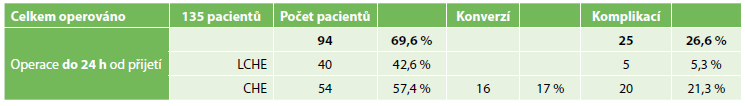
Results: Having compared patients with primary surgical treatment of acute calculous cholecystitis we found that twice as many patients after acute cholecystectomy done within 24 hours from admission developed 26% perioperative complications compared to those who had the surgery later than within 24 hours from their admission to the hospital (43.9%). We also found that there was a higher number of conversions from laparoscopic to open cholecystectomy in the group of patient undergoing cholecystectomy within 24 hours from admission.
Conclusion: Timing of the surgical treatment of acute calculous cholecystitis is essential for the development of postoperative complications. Acute laparoscopic cholecystectomy done by an experienced surgeon within 24 hours from admission of the patient to the hospital should be the golden standard, irrespective of the duration of the symptoms or severity of the acute cholecystitis. The sooner, the better.