Abstract
Introduction: Surgical resection is the method of choice in treating liver malignancies. In patients who are not suitable for radical surgical treatment, the radiotherapeutic system Cyberknife® is a viable treatment option. The aim of this study is to compare short- and long-term results of both treatment methods.
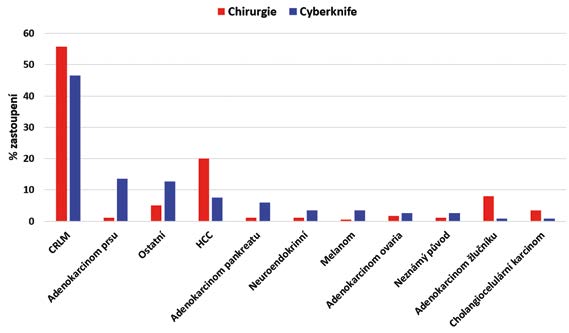
Methods: A retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data was performed, focused on patients undergoing treatment of liver malignancies either by surgical resection or by the Cyberknife® system from 2013 to 2016. Only patients treated using a single treatment method were included in the study.
Results: A total of 260 patients were analysed; 142 were treated by performing surgical resection and the remaining 118 using Cyberknife® radiotherapy. Median survival was 30.65 months for the surgical resection and 22.93 for the Cyberknife® therapy; median overall survival was 27.63 months. Three-year cumulative survival was 47.4% for the resection and 19.9% for radiotherapy. Kaplan-Meier analysis did not demonstrate a statistically significant difference in disease-specific survival between both groups (p=0.082, CI 95%). Results limited only to colorectal liver metastases showed a statistically significant difference in disease-specific survival (p=0.031, CI 95%).
Conclusions: Results of this study show statistically indifferent overall disease-specific survival of both groups. However, the significant difference in 3-year survival still indicates a predominant position of surgery in the diagnostic and therapeutic management of patients with liver malignancies. Nevertheless, Cyberknife® radiotherapy may actually represent a viable treatment alternative, particularly in patients unable to undergo surgical resection, although a longer follow-up period is necessary to obtain more robust results.