Abstract
Introduction: Differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) has a good prognosis and low mortality despite its growing incidence, which is particularly the case of microcarcinomas (T1a – up to 10 mm).
Methods: Retrospective analysis of overall survival of patients in the group of thyroid gland surgeries for differentiated forms of microcarcinoma in the period of 2006–2015 up to the present. An overview of contemporary therapeutic methods is included.
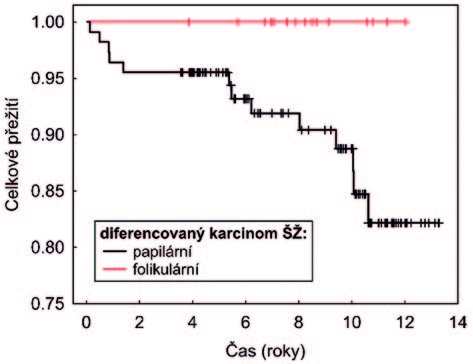
Results: Thyroid cancer was detected in 144 cases out of the total of 1820 patients with thyreopathy undergoing surgery (8%); DTC microcarcinoma was detected in 65 cases (45.1%) of all carcinomas. The papillary form was diagnosed in 59 cases (51.8% of all papillary cases), and the follicular form was found in 6 cases (37.5% of all follicular cases). Two cases of Hürthle cells cancer were found, both in a stage higher than T1. Overall 10-year survival of carcinomas >T1 was 86%, reaching 90% in the microcarcinoma group (Gehan Wilcoxon test: p=0.10675).
Conclusion: Differentiated microcarcinoma shows a very good overall survival. Provided that other criteria are satisfied, particularly unifocal occurrence without spreading through the gland casing and without any suspicion of nodal involvement, hemithyroidectomy is considered to be a sufficient procedure or the method of choice, respectively.