Abstract
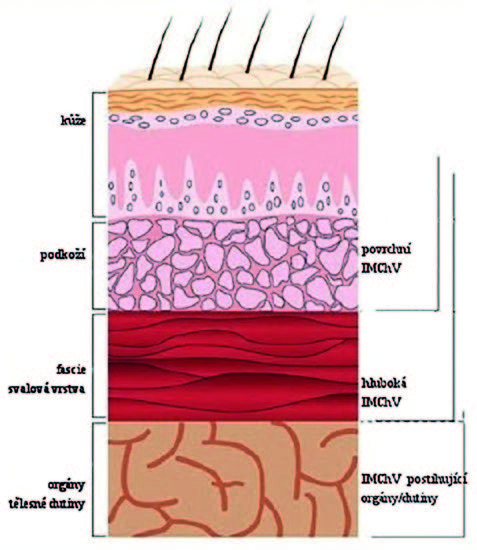
Surgical site infections are relatively common complications observed in patients during postoperative period. SSIs worsen the outcomes of the surgery, impair patient’s quality of life, increase morbidity and mortality after the surgery, the treatment become longer and more expensive. SSIs form around 18% of healthcare-associated infections. In developed countries the incidence of SSI varies from 2 to 15%. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors affect the incidence of SSI. CDC classification from 1992 differentiate 3 types of SSI: superficial, deep and organ/space infections. Controversial results of already published studies focused on the postoperative management of surgical wounds did not provide a space for strong clinical evidence-based guidelines. Early diagnostics of wound-healing complications related to high-risk patients provides for individualized surgery and postoperative management of the incision.ením pacientů se zvýšeným rizikem vzniku poruch hojení je možné individualizovat samotný operační výkon i pooperační management místa incize.