Abstract
Introduction: Retrospective analysis of a group of patients treated for pleural empyema in the Department of Surgery, University Hospital Pilsen, over the last ten years.
Method: We evaluated a group of patients treated for pleural empyema in the Department of Surgery, University Hospital in Pilsen, during the period 2007−2016. We focused on the demographic data of this group, the causes of empyema in these patients, surgical procedures performed in connection with empyema, the microbial species found in empyema, and, last but not least, on morbidity and lethality.
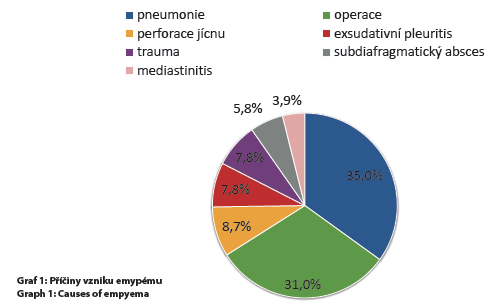
Results: We treated 103 patients with pleural empyema during the above period − 80 men (77.7%) and 23 women (22.3%) aged 23–83 years (average age 59.4 years). 64 patients had a history of surgical or invasive procedure (62.1%). The length of history was traceable in 55 patients (53.4%) and was 23.1 days on average, remaining unclear in the rest of the group. 1/3 of cases were metapneumonic empyemas, 1/3 postoperative empyemas and 1/3 of the cases were due to other reasons. The most commonly cultivated bacterial genus was Streptococcus, species Staphylococcus aureus. The most common surgery was chest drainage (51%). 13 patients died (lethality 12.6%) after surgery, the most common cause of death being sepsis; postoperative morbidity was 34%.
Conclusion: Pleural empyema is a serious condition with very high morbidity and lethality. Surgical procedures done to manage empyema are associated with a very high risk of necessary reoperation. Positive mycological culture from empyema seems to be associated with a higher risk of complications and death.