Abstract
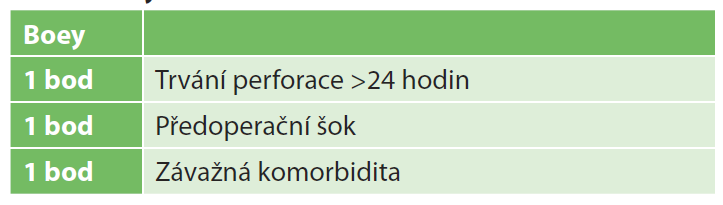
Introduction: Peptic ulcer is one of the most common diseases of the proximal gastrointestinal tract. Its complications are relatively common, the most serious one being peptic ulcer perforation with the incidence of about 10 cases per 100,000 population per year and the mortality rate of 10–40%. Surgical suture via laparoscopy or laparotomy is the only treatment option. The aim of the study was to compare the short-term results of laparoscopic and open repair of acute peptic ulcer perforation and evaluate the accuracy of the Boey scoring system in the Czech population.
Methods: Retrospective study conducted at the surgical department of the University Hospital Ostrava. The patients underwent laparoscopic or open repair of perforated peptic ulcer in 2017–2021.
Results: The study included 60 patients; laparoscopic repair was performed in 43.3% of the patients, and open repair in 56.7%. Postoperative morbidity was 70.0%, mild complications were reported in 23.3% of the patients, and severe complications in 16.7%. Patients undergoing the laparoscopic repair showed a higher incidence of mild as well as severe complications (26.9% vs 20.6% and 19.2% vs 14.7%) but also a higher incidence of an uncomplicated postoperative course. Overall postoperative mortality was 30.0% (laparoscopy 15.4%, laparotomy 41.2%). The study results confirmed the estimated baseline risk of mortality based on the Boey score.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic repair may be the procedure of choice for patients with no or low risk factors. Patients undergoing laparoscopy showed a higher incidence of mild and severe complications. The higher mortality of patients after open repair is related to their worse initial clinical condition. Preoperative determination of mortality risk using the Boey score is accurate and appropriate in terms of choosing the surgical approach