Abstract
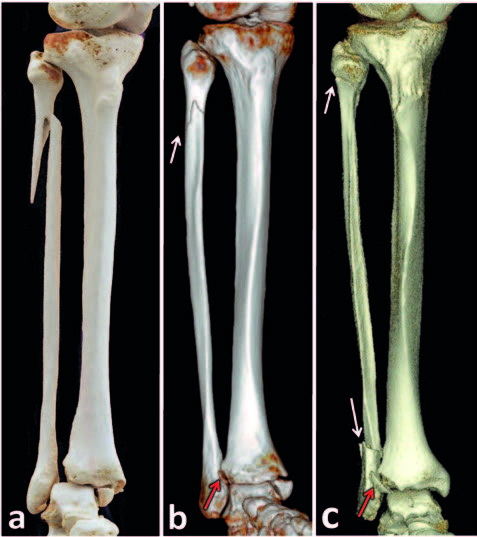
Maisonneuve fracture (MF) is defined as an ankle fracture-dislocation associated always with a fracture of the proximal quarter of the fibula and rupture of the anterior and interosseous tibiofibular ligaments. Other injuries are variable. Recent CT studies have demonstrated that MF is a far more complex injury than initially supposed. Therefore it is necessary to change substantially the current concepts related to this issue. MF is combined in about 80% of cases with a fracture of the posterior malleolus and also with malposition of the distal fibula in the fibular notch. An exact assessment of these injuries requires post-injury CT examination which should be used as a standard in MFs. The main goal of treatment is anatomical reduction of the distal fibula into the fibular notch. In case of avulsion of a larger fragment of the posterior malleolus, it is necessary to perform as the first step its reduction and fixation from the posterolateral approach and thus restore integrity of the notch. Closed reduction of the distal fibula is associated with malposition in up to 50% of cases and therefore open reduction from a short anterolateral approach is preferred. Accuracy of reduction should be always checked by postoperative CT scan