Abstract
Introduction: Triple negative breast carcinomas (TNBC) account for approximately 15−20% of all breast carcinomas. This subtype is characterised by an unfavourable prognosis with early locoregional recurrence a metastases. Only few studies have focused on the impact of local surgery on the overall therapeutic outcome. However, decisions are difficult to make in the case of TNBC, and no particular molecular subtype or marker exists that would make the decision-making process easier. The aim of our retrospective study was to analyse the TNBC surgical management outcomes at EUC Clinic in Zlin.
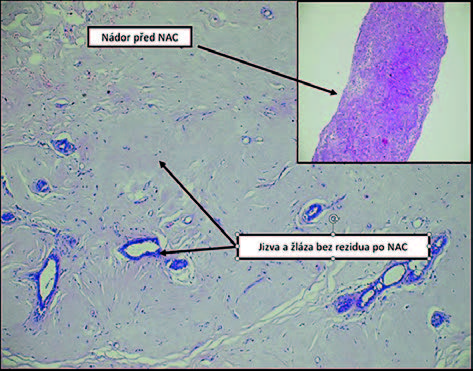
Methods: 440 women with breast carcinoma were operated on at EUC Clinic from 2014 to 2016, including 29 patients with TNBC; bilateral carcinoma was present in one case. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) was indicated in 6 cases. The tumour centre was marked with a clip. The extent of surgery depended on the residual size of the tumour. Sentinel lymph node biopsy was indicated in clinically negative lymph nodes; further management followed the Z0011 study if the biopsy was positive. Axillary lymph node dissection was performed after NAC. In all cases, surgery was followed by systemic chemotherapy, and by radiotherapy in the case of breast-conserving procedures.
Results: The group included 29 women and one patient with bilateral carcinoma, i.e. 30 cases of TNBC. Mean age was 57 years and median age was 55.5 years. Mean follow-up was 62.9 months, with the median of 69.9 month. NAC was indicated in 6 patients; complete pathological response was achieved in one case. NAC was followed by mastectomy in 5 cases including a bilateral procedure in one case, and by breast-conserving surgery in one case. Axillary dissection was performed in all cases. Breast-conserving surgery and sentinel node biopsy predominated in the group (16 cases). Local recurrence was observed in 4 cases, 2 times as an isolated local recurrence after one year and 2 times as part of generalization, always after mastectomy. Six patients died of generalized disease. No regional recurrence was observed.
Conclusion: TNBC is characterised by a worse prognosis and a higher rate of local recurrence. As confirmed by our study, the results of breast-conserving surgery can be comparable to those of radical procedures, and thus radical surgery should be indicated prudently.