Abstract
Introduction: During the last decades, simultaneously with the development of surgical technique, modern equipment and perioperative management, there has been a significant improvement in postoperative outcome. Despite this, infectious complications and perioperative bleeding remain the leading causes of postoperative morbidity and mortality in HPB surgery.
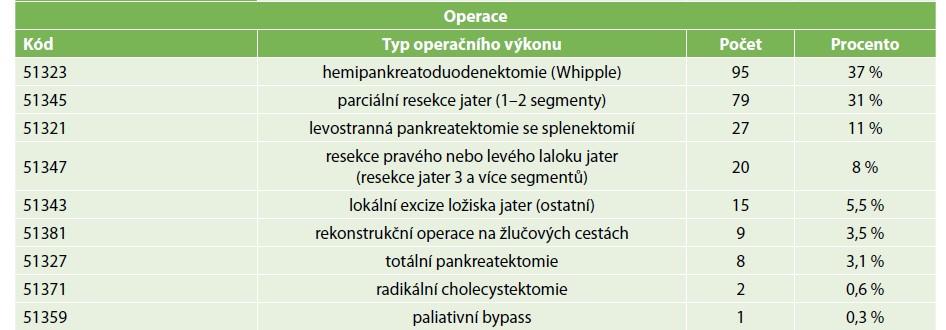
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study over a three-year period in 256 patients who underwent surgery of the pancreas, liver, gallbladder, or bile ducts. We monitored perioperative blood loss, the number of administered transfusions, the type and severity of postoperative complications, the number of reoperations and the number of readmissions.
Results: The average blood loss was 457 ml. We administered transfusions to 39 patients (17%). We confirmed the hypothesis that the presence of blood loss statistically significantly increases the development of deep intra-abdominal infections (p=0.0188). Morbidity increases with increasing blood loss (p=0.0168). We confirmed a statistically significant difference in the blood loss between the groups with and without complications (p=0.001). Postoperative 30-day mortality was less than 1% (n=2). There were 15 (6%) reoperated patients, seven for acute bleeding and eight for infectious complications. The length of hospital stay was statistically significantly longer in patients who received transfusions – erythrocytes (p=0.023), and plasma (p=0.011). We readmitted 12 patients, three patients died during rehospitalization (the 90-day mortality rate was 2%, n=5). A total of 59% patients in our group were classified as ASA III.
Conclusion: With increasing blood loss, morbidity (development of intra-abdominal infections) increases significantly, but despite this, overall postoperative mortality remains low. Early postoperative bleeding is the cause of more than half of reoperations. The length of hospitalization increases significantly with the number of transfusions administered.