Abstract
Introduction: A reproducible and simple model is essential for verifying gastric conduit vitality before esophagectomy. Ischemia is a major cause of esophagogastric anastomotic dehiscence and leakage. Ischemic conditioning of the stomach prior to esophageal surgery has been shown to lower the incidence of postoperative complications, including anastomotic leakage. However, the optimal timing and technique of ischemization remain uncertain.
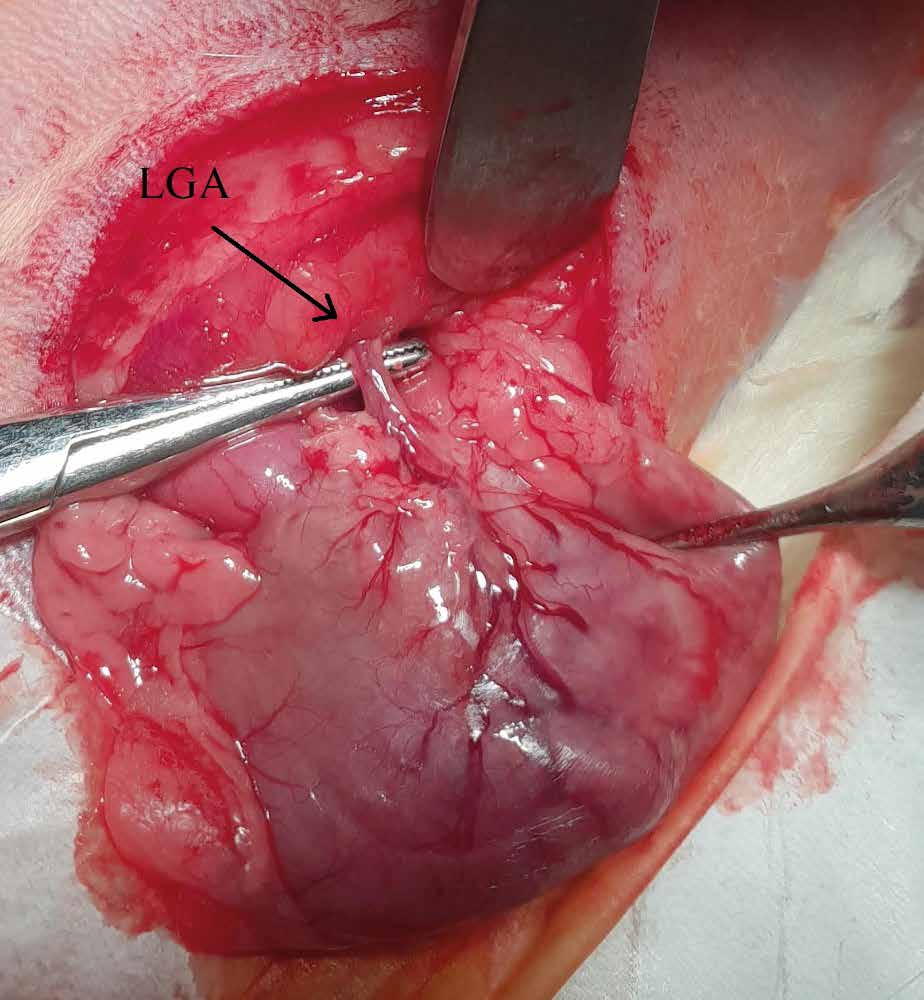
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (n=24) were randomly divided into four groups: ischemic group – samples collected 1 hour after ischemia (I1H), ischemic group – samples collected 1 day after ischemia (I1D), ischemic group – samples collected 7 days after ischemia (I7D), and control group (C). Ischemia was induced by ligation of the left gastric (LGA) and short gastric arteries (SGA). The samples were verified using histological and macroscopic analysis, and the number and percentage of immunocompetent cells were determined.
Results: One hour after ischemization (I1H), ischemic denudation with mucosal erosion was observed, and the total number of eosinophils was significantly higher (p<0.05) in the I1H group compared to the I1D and I7D groups. One day after ischemia (I1D), there was a reduction in the inflammatory response with partial regeneration of gastric mucosa. In the I7D group, nearly complete architectural regeneration of mucosal epithelium was documented. The total count of polymorphonuclears was significantly lower (p<0.05) compared to the I1D group.
Conclusion: Ischemic mucosal injury after LGA and SGA ligation was observed dominantly in the I1H and I1D groups, but not in I7D group. In conclusion, this study presents a simple method for verifying gastric ischemic changes.