Abstract
Introduction: The aim of the study was to perform a retrospective analysis of patients who had undergone laparoscopic resection for pancreatic cancer (PC) at the Department of Surgery of the Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University and University Hospital Brno, Czech Republic from 2010 to 2023.
Methods: Forty-six patients with laparoscopic (n=19) or open (n=27) distal pancreatectomy (DP) for PC were included. Both groups were statistically evaluated and compared in the following parameters: clinical stage, tumor grade, nodes examined by the pathologist, blood loss, duration of surgery, three-month morbidity and mortality, length of ICU stay, overall length of hospital stay, readmission rate and overall survival.
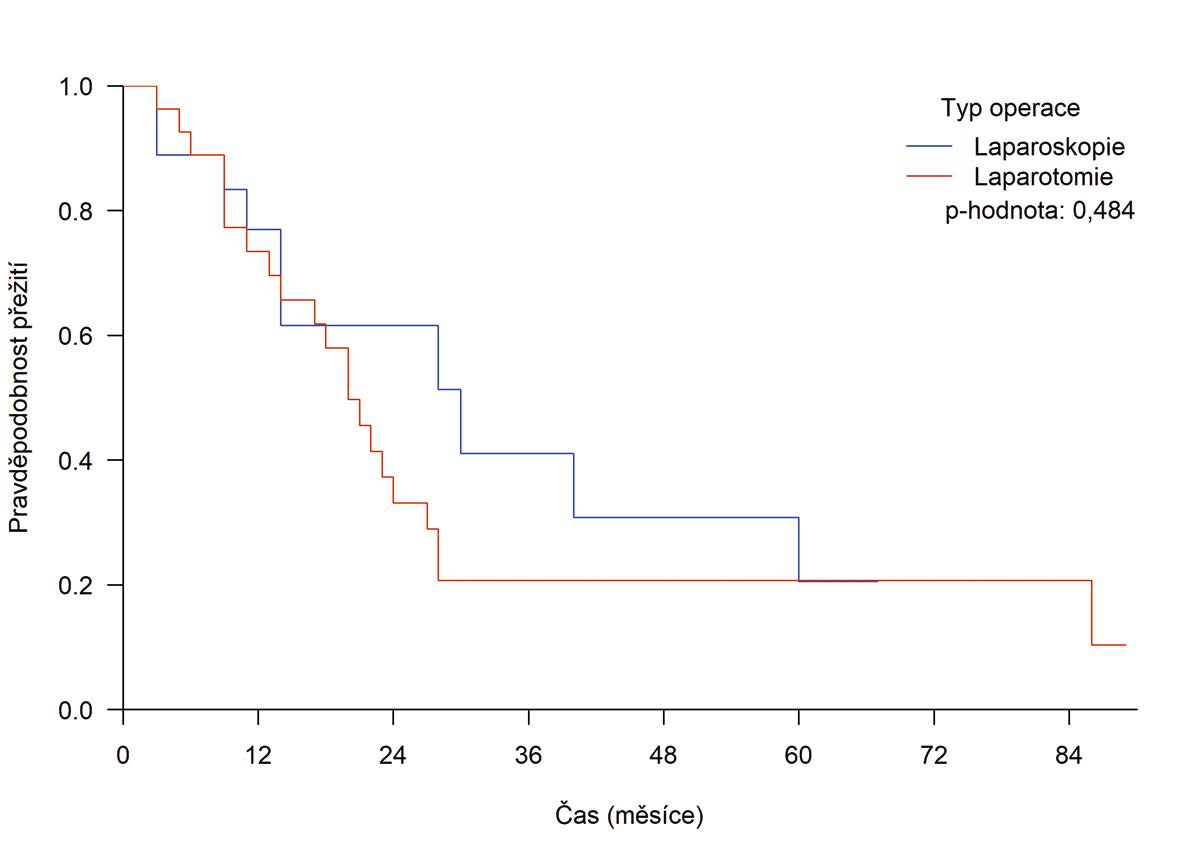
Results: There were more T3 tumors in the open DP group (81.5% vs 57.9%, p=0.035). The rate of dedifferentiated (G3) tumors was higher in the open DP group (18.5% vs 5.3%, p=0.354). The mean number of nodes examined by the pathologist was equal in both groups (open DP 15.1 (min– max, 3–39) vs lapDP 15.6 (min–max, 5−39). Laparotomy was associated with a higher mean blood loss (531 ml vs 198 ml, p=0.002). However, it was shorter on average (190 minutes vs 216 minutes, p=0.006). Clinically relevant complications (Dindo III and higher) and POPF (types B and C) were observed in 10/46 (21.7%) and 14/46 (30.5%) cases without any statistically significant difference between both groups (p=0.489 and p=0.241, respectively). The median ICU stay was similar for lapDP and open DP (median: 5.0 days vs 6.0 days, p=0.396). Overall length of hospital stay was identical in both groups (median: lapDP 12.0 days vs open DP 12 days, p=0.920). The three-month readmission rate was 5/46 (10.9%). One-, 2-, 3- and 5-year overall survival probability after laparoscopic and open DP was 76.9% (95% CI 59.4−99.7%), 61.5% (95% CI 41,1−92.2%), 41.0% (95% CI 20,5−82.2%) and 20.5% (95% CI 6.2−68.2%), and 73.4% (95% CI 58.3−92.4%), 33.1% (95% CI 18,9−57.9%), 20.7% (95% CI 9.5−44.9%) and 20.7% (95% CI 9.5−44.9%), respectively. No statistically significant difference was observed between both groups (p=0.484).
Conclusion: When comparing lapDP and open DP performed for pancreatic cancer, our experience confirmed that lapDP was particularly suitable for patients with smaller tumors located further from the porto-mesenteric axis. The laparoscopic approach was associated with lower blood loss, reduced length of ICU stay, comparable morbidity and overall survival. The relatively long length of hospital stays, surprisingly identical in both groups, prompted us to implement the ERAS (Enhanced Recovery After Surgery) protocol in this surgical field.