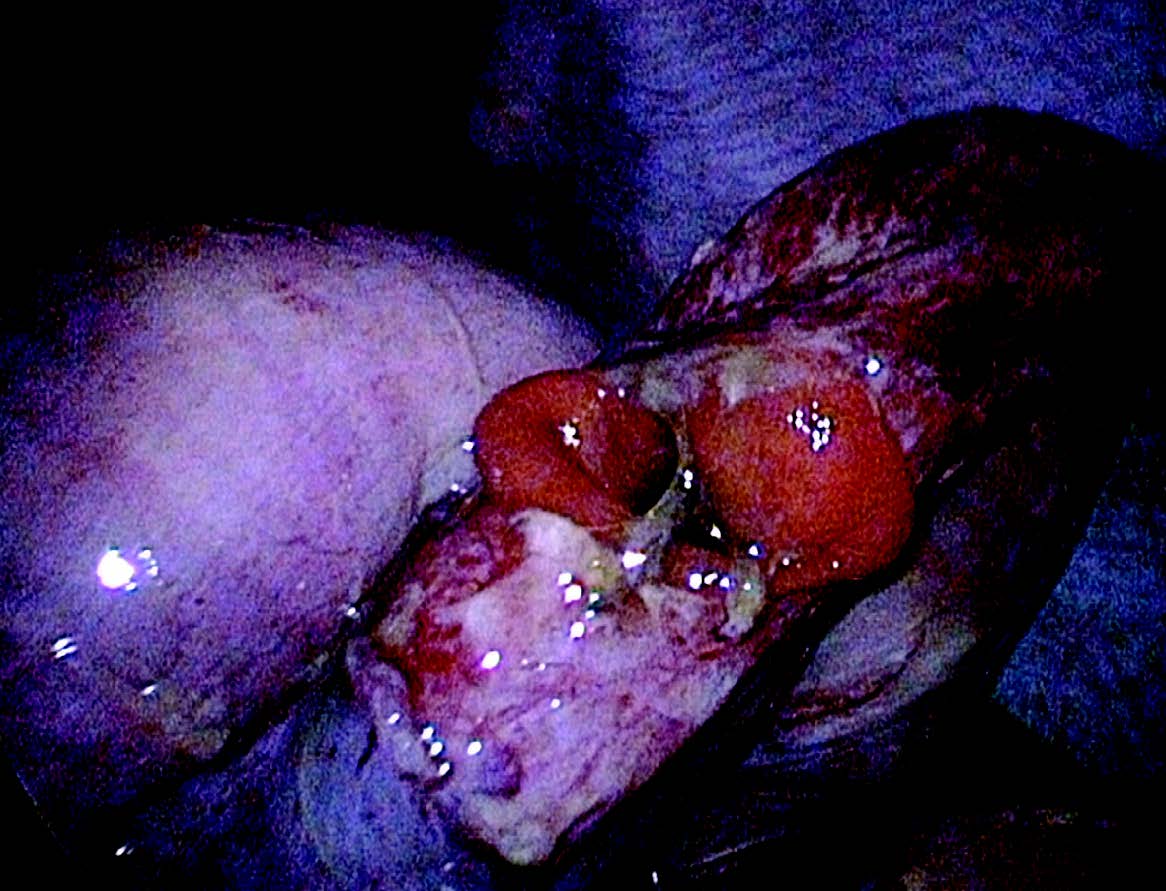
Abstract
Minimally invasive techniques have now become standard for the treatment of many surgical conditions in children. There are a few studies that describe the utility of laparoscopy in BAT in children. In this article, we describe the complete laparoscopic surgical treatment of two patients after a single blunt abdominal trauma, both with bowel perforation. In both cases, the perforation was identified and closed, one laparoscopically with an ongoing suture, the second jejune perforation was closed by laparoscopic-assisted techniques. Both patients had an uneventful postoperative recovery.
Therapeutic laparoscopic treatment of patients with upper gastrointestinal perforation is feasible. We hypothesize, that diagnostic laparoscopy provides important information for the treatment of children with abdominal trauma and is accompanied by improved diagnostic accuracy, reduction of nontherapeutic laparotomy rates, and a reduction of morbidity. Minimally invasive surgery in children after BAT is suitable for hemodynamic stable patients, could improve pain scores, cosmetic effect, shorter hospital stays, shorter operative times and shorter return to school/activities. However, at any point in the patient’s care, in case the unstable hemodynamic is encountered, exploratory laparotomy is the procedure of choice.